In the presence of signs and symptoms of illness, doctors prescribe many laboratory tests to confirm the assumptions and make a diagnosis. In the list of appointments, patients can get HPV analysis: what, why and when it is prescribed - not everyone can respond.
What is HPV?
The human papillomavirus, HPV, is a complete group of virus - like infectious diseases. Scientists know more than 100 types of this virus, not all of which are dangerous to humans. Most are invisibly present in the body for a long time, leading to miscarriage. However, about 14 types of this virus are oncogenic - they stimulate the development of malignant neoplasms. When making a diagnosis, doctors always pay attention to the type of HPV, its oncogenicity, which further determines the actions and nature of treatment.
Human papillomavirus - types
The papilloma virus is usually divided into types depending on the risk of stimulating oncological development. Taking this factor into account, there are three main groups of HPV:
- Non-oncogenic- never causes the development of malignant tumors.
- Low risk oncogenic- can, under certain conditions, stimulate the development of cancer: 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
- High risk of oncogenic- when infected with these types of HPV, it is difficult to avoid the development of malignant tumors. Oncogenic human papilloma viruses: 16, 18, 31, 35, 33, 45, 58, 59, 52.
How is the human papilloma virus transmitted?
Knowing how papillomavirus is transmitted can reduce the risk of infection. In practice, however, this is difficult to avoid. In the vast majority of cases, transmission occurs with the onset of sexual activity: sexual intercourse is the main mode of transmission of the virus. Transfusion can also be done during a kiss, when there are microcracks and scratches on the surface of the lips. You can also become infected if you break the hygiene rules when visiting public places:
- saunas;
- swimming pool:
- baths;
- and also when someone else uses a toothbrush, towel, razor.
Infection can also occur when the baby passes through the maternal pathways of infection during childbirth. Experts do not rule out the possibility of transmitting the virus by excluding contact: it is unstable, but is able to maintain some activity.Factors that trigger HPV infection include:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- large number of sexual partners;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- reduced immunity.
The human papilloma virus - symptoms
Human papilloma virus can be invisible in the body for a long time. The incubation period, according to experts, can last from 2 months to 2 years. The disease progresses himperceptibly: there are no clinical signs, and the main diagnostic methods indicate the norm. One in three patients, thanks to their immune system, recovers within 6-12 months from the moment of infection.
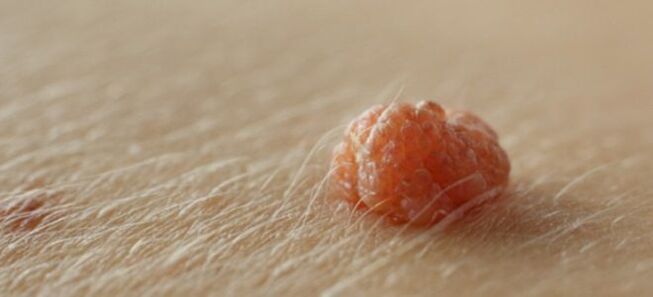
The clinic of HPV damage to the body is reduced to the appearance of skin formations. Patients notice papillomas, warts and condylomas on their skin. Their location can be different and corresponds to where the virus enters the body: genitals, surface of hands, lips. These formations look like papillary outgrowth, sometimes resembling cauliflower externally. The outgrowths are painless, but with friction and injury they can cause pain and bleeding.
Why do I need an HPV test?
After telling us about the virus, let's move on to information about HPV analysis: what kind of research it is, how it is done and in what cases it is prescribed. First, we note that if human papillomavirus is suspected, the analysis helps to confirm or refute the assumptions. This type of research has the following goals:
- identification of high risk oncogenic HPV;
- declaration / denial of persistence of a particular type of HPV;
- assessment of cancer risk in patients with dysplasia of the epithelial layer of the cervix.
In addition to the named reasons for the examination, the HPV analysis (illustrated above) may be shown in the following cases:
- Primary screening for cervical cancer in women over 30.
- Evaluation of the results of surgical treatment of intraepithelial neoplasia.
- Suspicious results of cytological examination of gynecological smears.
What tests should I do for HPV?
There are several methods for determining the presence of the papilloma virus in the body. However, in most cases, doctors resort to PCR. If HPV analysis is required, this examination is performed directly on patients. Various biological body fluids can be used as examination material:
- blood;
- urine;
- amniotic fluid (when a disease is diagnosed during pregnancy).
Talking about HPV analysis, what it is and how it is performed, it is necessary to note the possibility of studying tissue content. So, during colposcopy, the doctor carefully examines the mucous membrane of the cervix. The presence of small papillomas on them is direct evidence of HPV damage to the body. To confirm, a small piece of tissue is taken for examination under a microscope to exclude malignancy.
HPV diagnostic methods
HPV diagnostics is a set of measures aimed at locating the presence of the virus and determining its type. For this purpose, the following techniques are used:
- Digene test- modern precise method. With its help, the concentration of the virus in the body, the type and oncogenicity can be established. Material for research is scraped from the mucous membrane of the urethra or vagina. It is often used in combination with cytology.
- PCR diagnostics of HPV- a simple and affordable and widely used diagnostic method. The material used is the patient's blood or urine. The sample is assumed to detect viral traces of DNA.
- Cytology Examination- examination of the smear under a microscope. The assessment criterion is the presence of modified cells in the smear - dyskeratocytes and coilocytes.
- Detection of antibodies to HPV- helps identify virus infection in the early stages. The disadvantage is that the concentration and type of virus cannot be established.
- Histological examination - examination of a sample of the affected tissue to determine the type of HPV and its oncogenicity.
The human papilloma virus - how to test?
Prior to the examination, even during the issue of the referral, the doctors tell the patient in detail how the HPV test is performed in a particular case. Depending on the examination methods and materials used, the analysis algorithm may differ. Preparing for research is very important. Proper application of all points of the preparatory measures allows you to obtain the objective results of the analysis and eliminate the need for repeated application.
Preparing for the HPV analysis
Prior to the analysis of HPV, the patient must meet a number of conditions. In this case, the method of the survey and the type of material for analysis are of decisive importance. It is represented by:
- blood;
- urine;
- swab from the vagina or urethra.
Depending on the type of biological fluids being studied, the patient is given suggestions on how to prepare for the analysis the day before. The examiner's task is to fully follow the rules of preparation. This will avoid getting false results, and in some cases false positives, when the result indicates the presence of HPV in its absence.
HPV blood test
Talking about how the HPV test is performed, it should be noted that in most cases the patient's blood is used for it. The study is performed on an empty stomach: 10-12 hours before the estimated time of taking the material, the patient is not allowed to eat; as a drink, you can use ordinary water without gas. 2-3 days before the day of analysis, it is forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, fatty foods and junk. Except in this case, a diagnosis of HPV by blood will allow you to get accurate test results.
HPV smear analysis
This method is used more frequently to examine the fair sex. Before women are tested for HPV, they are prepared for this test. The doctor gives the patient all the rules of preparation in detail.In this process, the following key points can be highlighted:
- Smear is taken before the start of a course of antibiotics or 2. 5 weeks after the end of treatment.
- On the day of sampling, it is forbidden to toilet the external genitalia using chemical hygiene products.
- It is forbidden douche, enter vaginal suppositories.
- One day before you take the matter, you must refrain from intercourse.
- It is appropriate to analyze in the middle of the cycle; it is forbidden to study during the ovulation period.
Decoding the HPV analysis
Only a doctor can determine HPV test results correctly. The specialist evaluates not only the quantitative value of the indicators, but also the clinical picture, possible signs of infection. Getting a complete picture of what is happening helps you to choose the right medications and effective treatment methods. At the same time, it is important to take into account the severity of timely diagnosis and treatment: with the age of the patient, the risk of developing malignant neoplasms increases.
Quantitative analysis of HPV
When HPV testing is performed using quantitative analysis, decoding involves establishing the concentration of the virus at the time of the study. This helps determine the right tactics for patient management. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) measures the amount of HPV DNA in a test sample. This is necessary for continuous dynamic monitoring of a specific type of human papilloma virus.
However, even those familiar with the HPV analysis, what it is and how it is performed, cannot independently understand the results. This must be done in conjunction with the patient examination and other examinations. In making an assessment, experts adhere to the interpretation of the following indicators:
- lg< 3- the risk of developing dysplasia is low;
- lg 3-5- clinically significant result, there is a risk of developing cervical dysplasia;
- lg >5- high probability of dysplasia, possibly in the early stages of the disease.
Qualitative HPV analysis
HPV analysis of high oncogenic risk is performed using this technique. Helps identify the 16th and 18th types of HPV. These forms of the virus often cause genital cancer in women and squamous cell carcinoma, genital warts, and cervical dysplasia. HPV DNA detection efficiency reaches 98%. The conclusion suggests a response to the manifestation of each type of virus. There are two possible outcomes: found / not found.














































































